Create a source
A source can be created from different origins.
Table Name Requirements
The names of the tables in the source must not contain the / character.
File source
Data can be uploaded directly from a file (CSV, XLSX, …). A source imported in this manner is referred to as a file source.
The file source must be encoded in UTF-8, use commas ,, semicolons ; or tab \t as column separators, and start with a single header line, containing the column names.
Attention! Ensure that each row contains the same number of columns.
To create a file source we must upload the relative files in the designated modal:
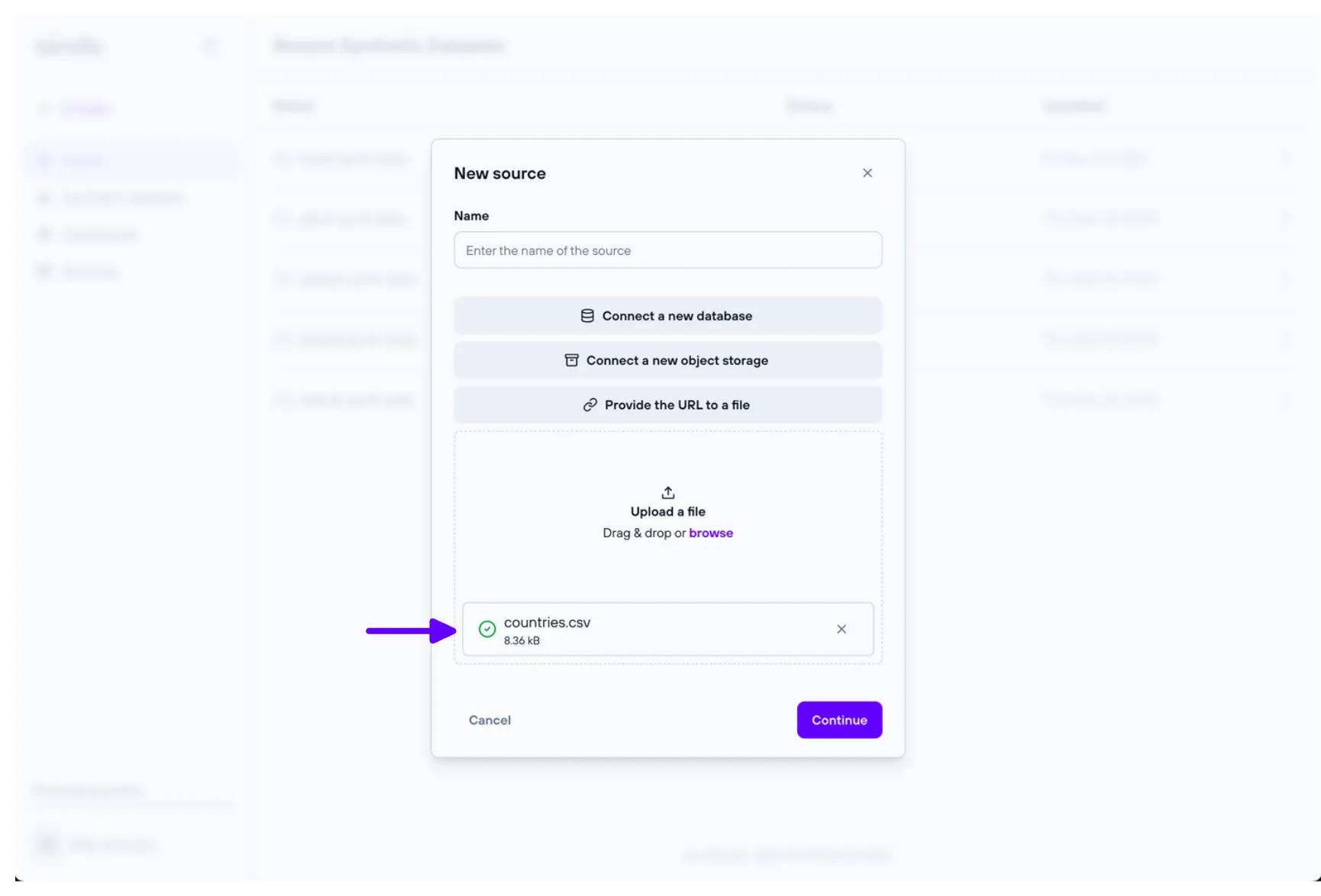
Table relations
Note that when uploading multiple files, the primary key and the relations between columns should be specified by the user through the configuration stepper.
Column type inference
When uploading a file, the column type will be inferred automatically. Users can manually adjust column types through the configurator stepper.
Size requirements
- Each file must be less than 100MB in size.
- Each file must correspond to a single table, except for Excel and OpenOffice formats, where each sheet corresponds to a single table. So the only way to import relational DB file sources is as separate files, which have to be linked manually in the configurator stepper.
File format requirements
Aindo’s platform supports the following formats for file sources:
- .csv
- .parquet
- .tsv
- .xls
- .xlsx
- .xlsm
- .xlsb
- .ods
- .odf
- .odt
Every file that is not format compliant will be rejected.
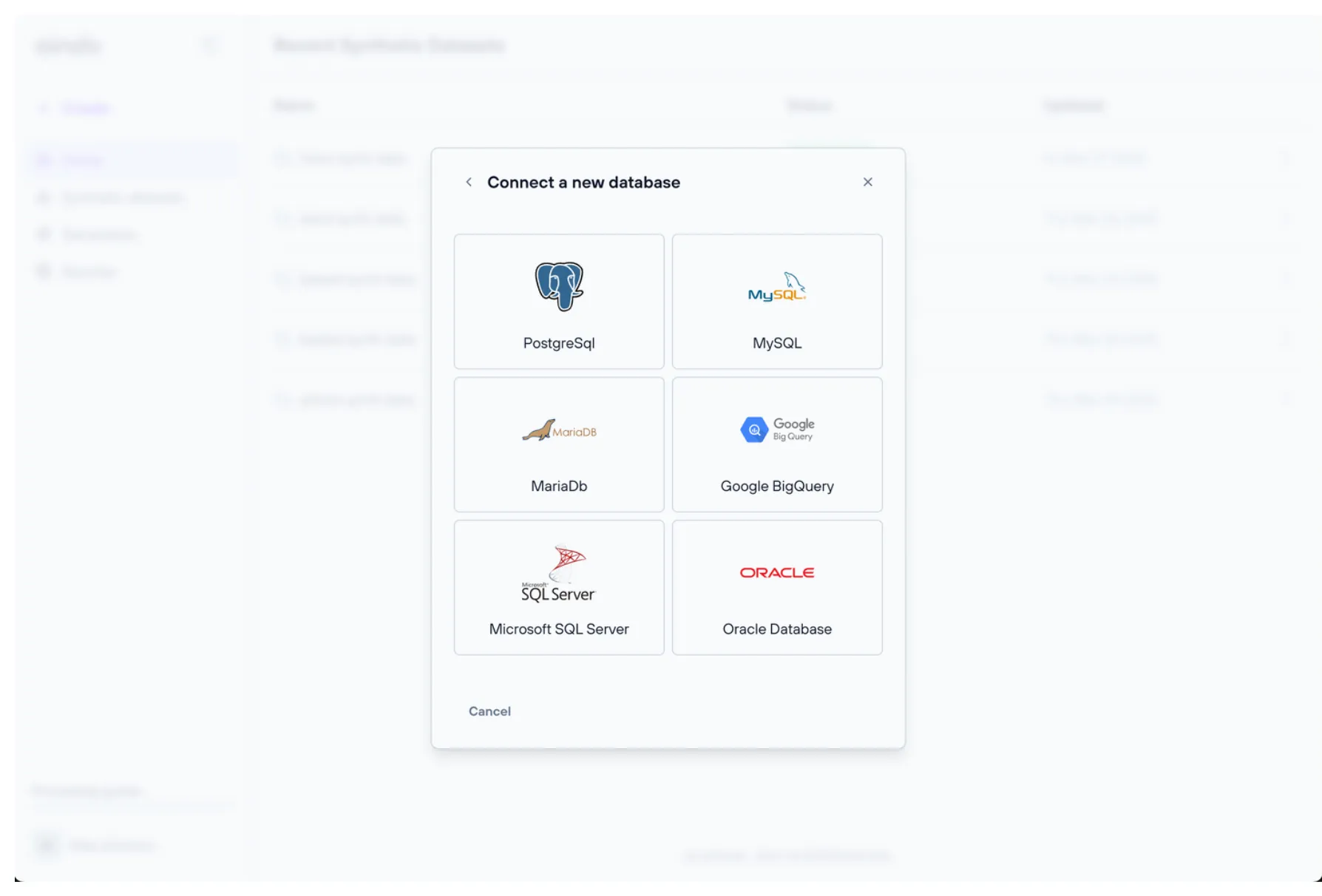
Remote database source
A remote database can be used as a source (note that the database must have at least read permissions). Aindo’s platform is compatible with the following database systems:
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- Google BigQuery
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Oracle Database
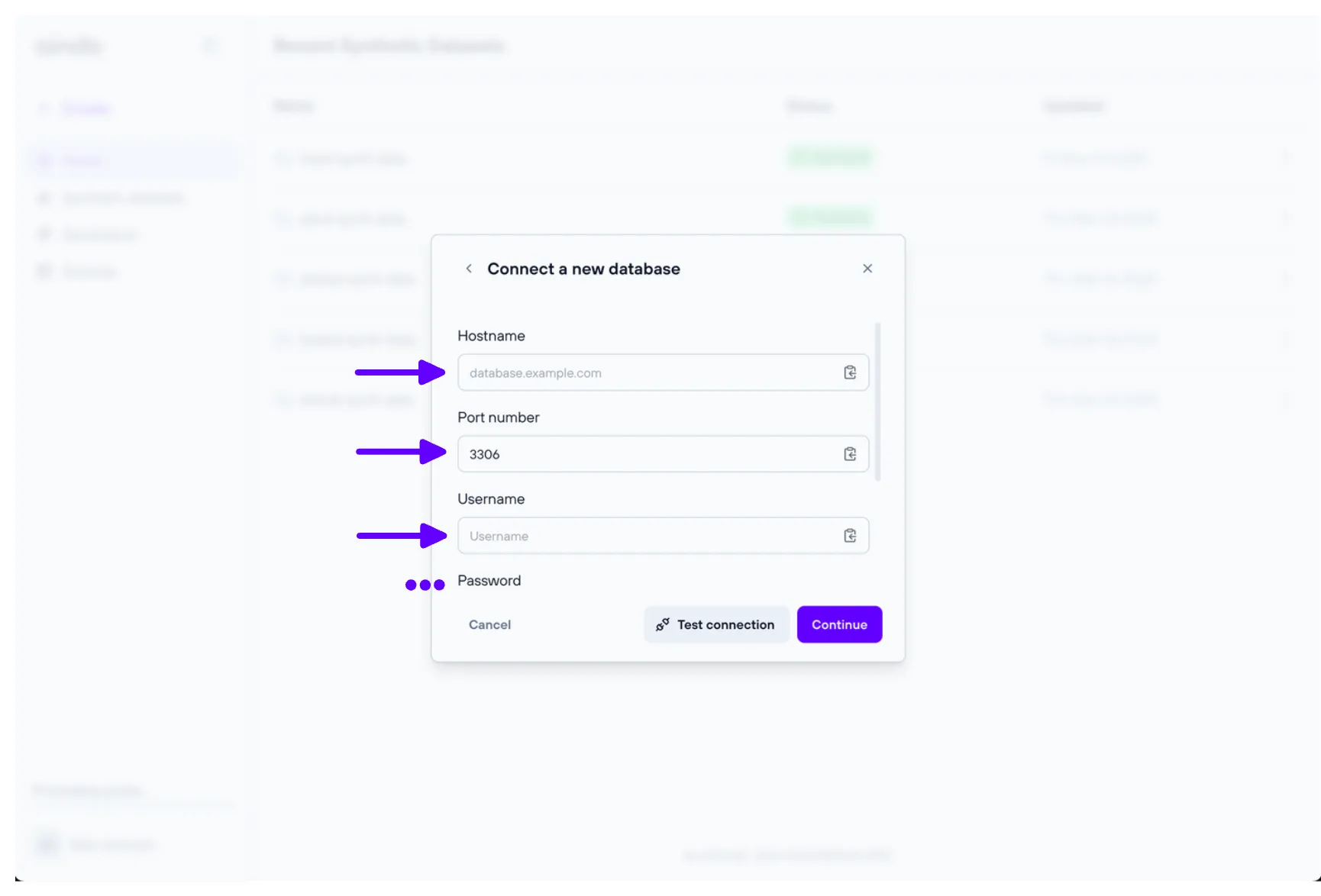
To verify that you have entered the correct settings, you can use the “Test Connection” button to check if the remote database accepts the connection.
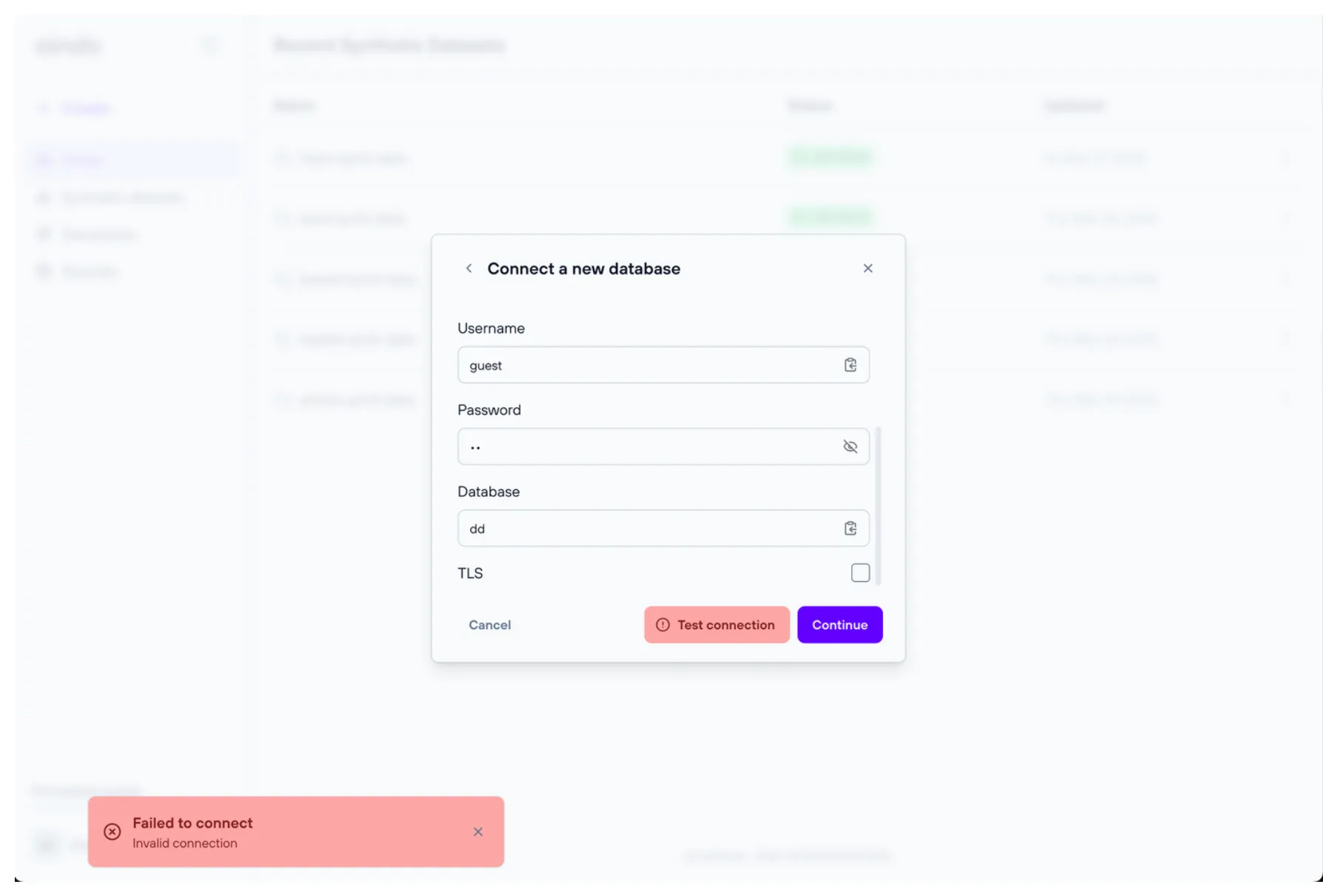
For detailed information about required permissions for remote database sources, see Connector Permissions.
Supported versions
We support all active and maintained versions of the databases listed above. For a detailed list of supported versions, please refer to the table below:
| Database | Supported versions |
|---|---|
| PostgreSQL | 17 (current), 16, 15, 14, 13, 12 |
| MySQL | 8.4 (current), 8.0, 5.7 |
| MariaDB | 11.5 (current), 11.4, 11.2, 10.11, 10.6, 10.5 |
| Google BigQuery | current |
| Microsoft SQL Server | 2022 (current), 2019 |
| Oracle Database | 23ai (current), 21c, 19c, 18c, 12c (R2) |
Supported data types
This section lists the SQL data types fully or partially supported for each database system you can connect to from Aindo’s platform. Notes clarify partial support, and any types not listed are considered unsupported.
| Database | Supported | Partially supported |
|---|---|---|
| PostgreSQL | BIGINT, BIGSERIAL, BOOLEAN, CHAR, VARCHAR, TEXT, FLOAT4, FLOAT8, INT2, INT4, INT8, NUMERIC, SERIAL2, SERIAL4, SERIAL8, DATE, TIME, TIMETZ, TIMESTAMPTZ | |
| MySQL / MariaDB | BOOLEAN, TINYINT, SMALLINT, MEDIUMINT, INT, BIGINT,DECIMAL, FLOAT, DOUBLE, DATE, TIME, DATETIME, TIMESTAMP, YEAR, [NATIONAL] CHAR, [NATIONAL] VARCHAR, TEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, LONGTEXT, ENUM | |
| Google BigQuery | BOOL, DATE, DATETIME, INT64, NUMERIC, BIGNUMERIC, FLOAT64, STRING, TIME, TIMESTAMP | STRUCT 1 |
| Microsoft SQL Server | TINYINT, SMALLINT, INT, BIGINT, BIT, NUMERIC, FLOAT, REAL, DATE, DATETIMEOFFSET, DATETIME, SMALLDATETIME, CHAR, VARCHAR, TEXT, NCHAR, NVARCHAR, NTEXT | TIME, DATETIME2 2 |
| Oracle Database | CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, DATE, CLOB, NCLOB, NUMBER, FLOAT, BINARY_FLOAT, BINARY_DOUBLE | TIMESTAMP 2, TIMESTAMP WITH [LOCAL] TIME ZONE 2,3 |
- Nested fields are mapped to standalone columns.
- Fractional second precision is supported up to 6 decimal places.
- Named time zones are not supported.
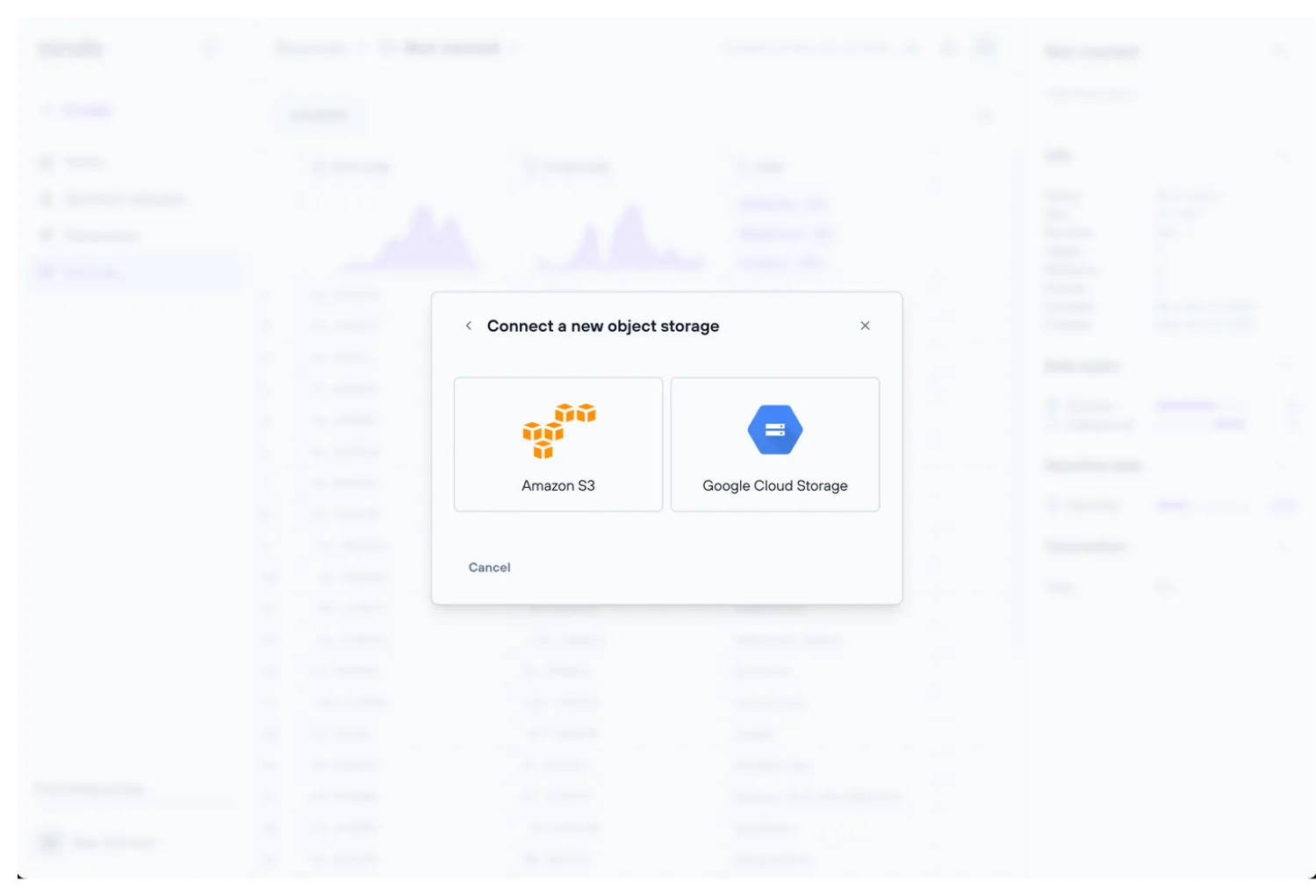
Remote object storage source
A remote object storage can be used as a source (note that the object storage must have at least read permissions). Aindo’s platform is compatible with the following object storage systems:
- Amazon S3
- Google Cloud Storage
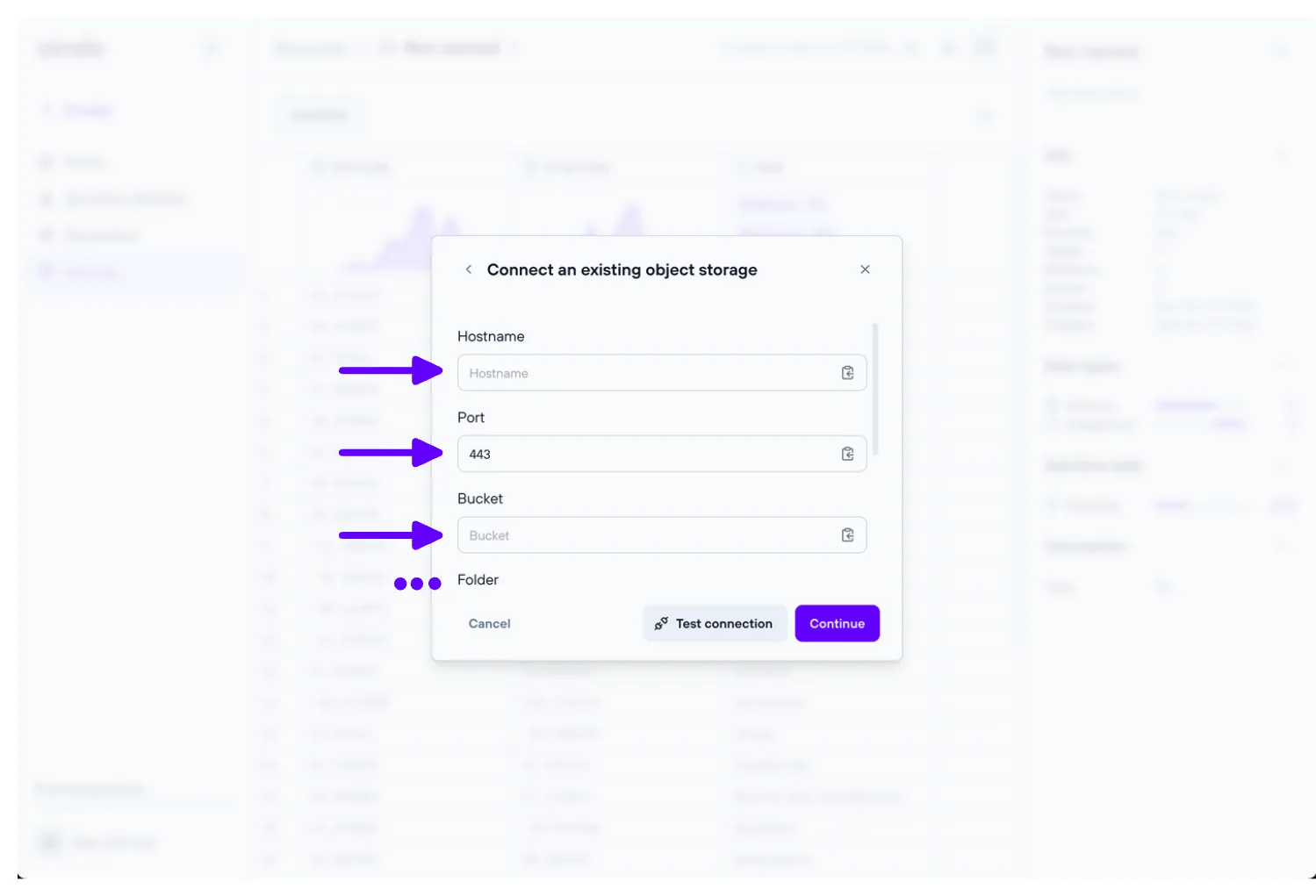
To verify that you have entered the correct settings, you can use the “Test Connection” button to check if the remote database accepts the connection.
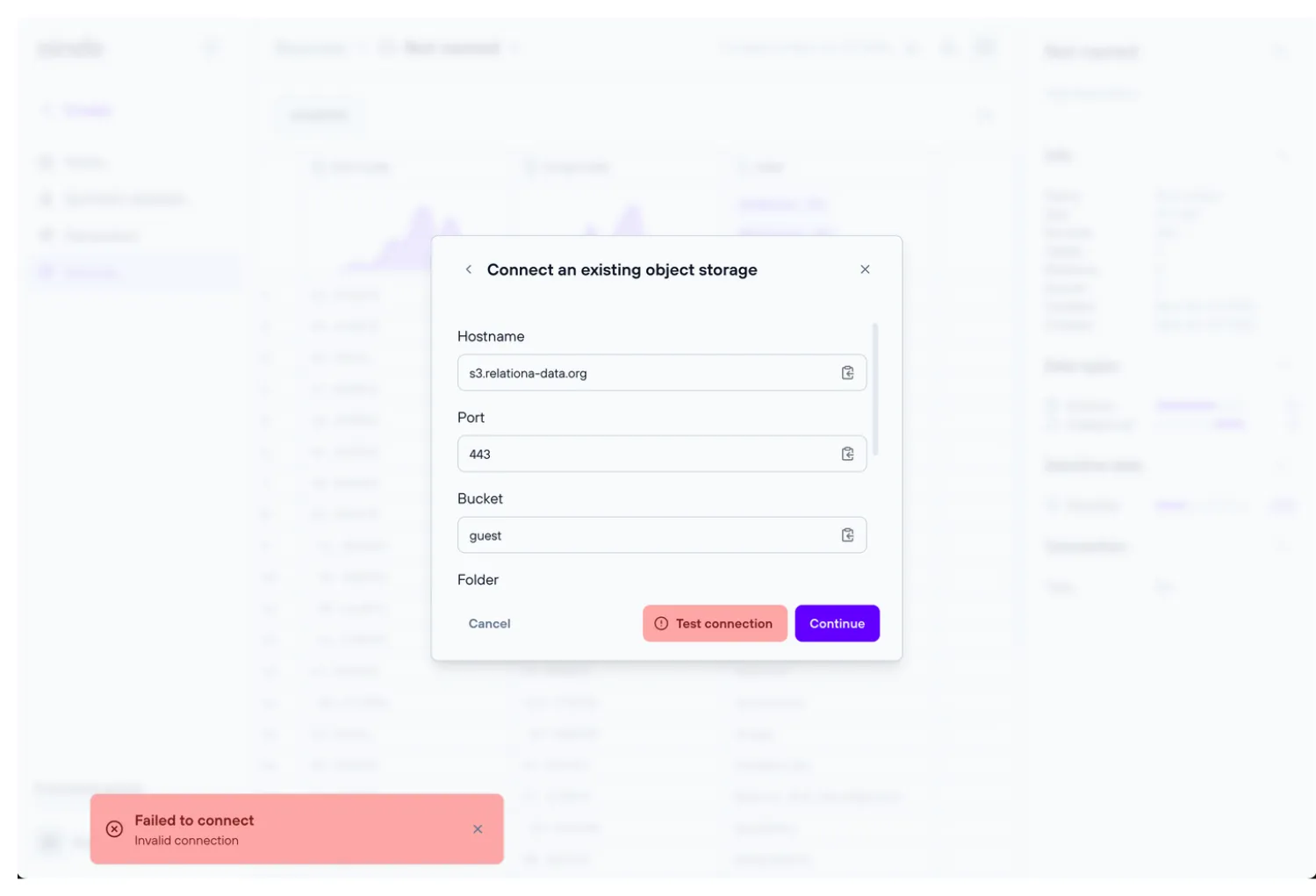
When using an object storage as source, table names are inferred from object keys found on the storage. When files are selected through the file browser, extensions such as .csv are automatically stripped from the table name.
File browser
After a successful connection test, a file browser dialog opens, allowing you to browse the contents of the bucket and select specific files to import.
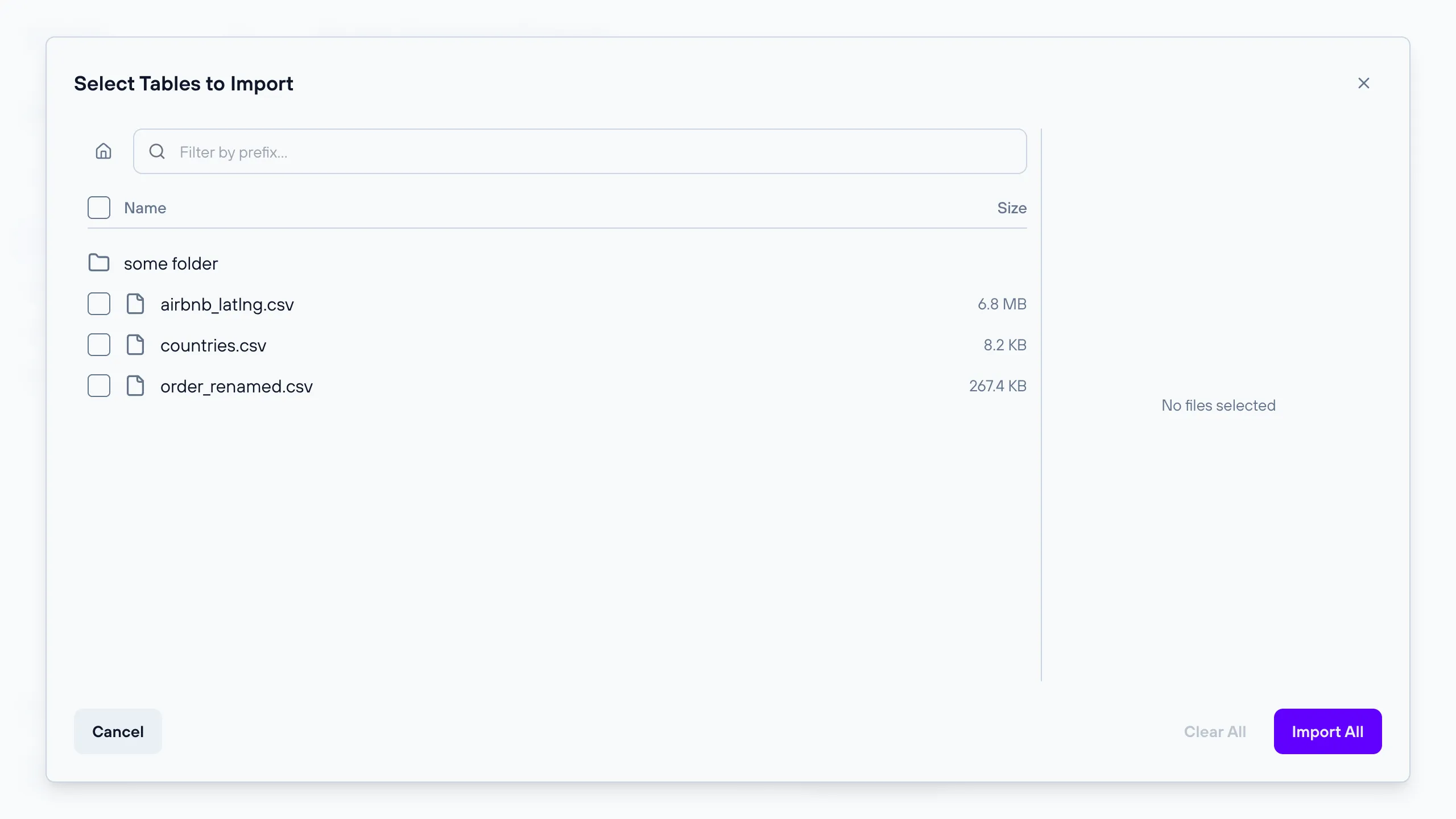
The left panel displays the bucket contents. You can:
- Navigate folders by clicking on them, and use the breadcrumb trail to go back
- Filter by prefix using the search field to narrow down the listed files
- Select files individually by clicking on them, or use “Select All” to select every file in the current view
The right panel shows your current selection. For each selected file you can:
- Rename the table by clicking the edit icon — duplicate table names are not allowed
- Remove the file from the selection by clicking the remove icon
When you are done, click “Import N tables” to import only the selected files, or “Import All” to import every file in the current folder (subfolders are not included). If the import fails, the dialog stays open so you can adjust your selection without starting over.
For detailed information about required permissions for remote object storage sources, see Connector Permissions.
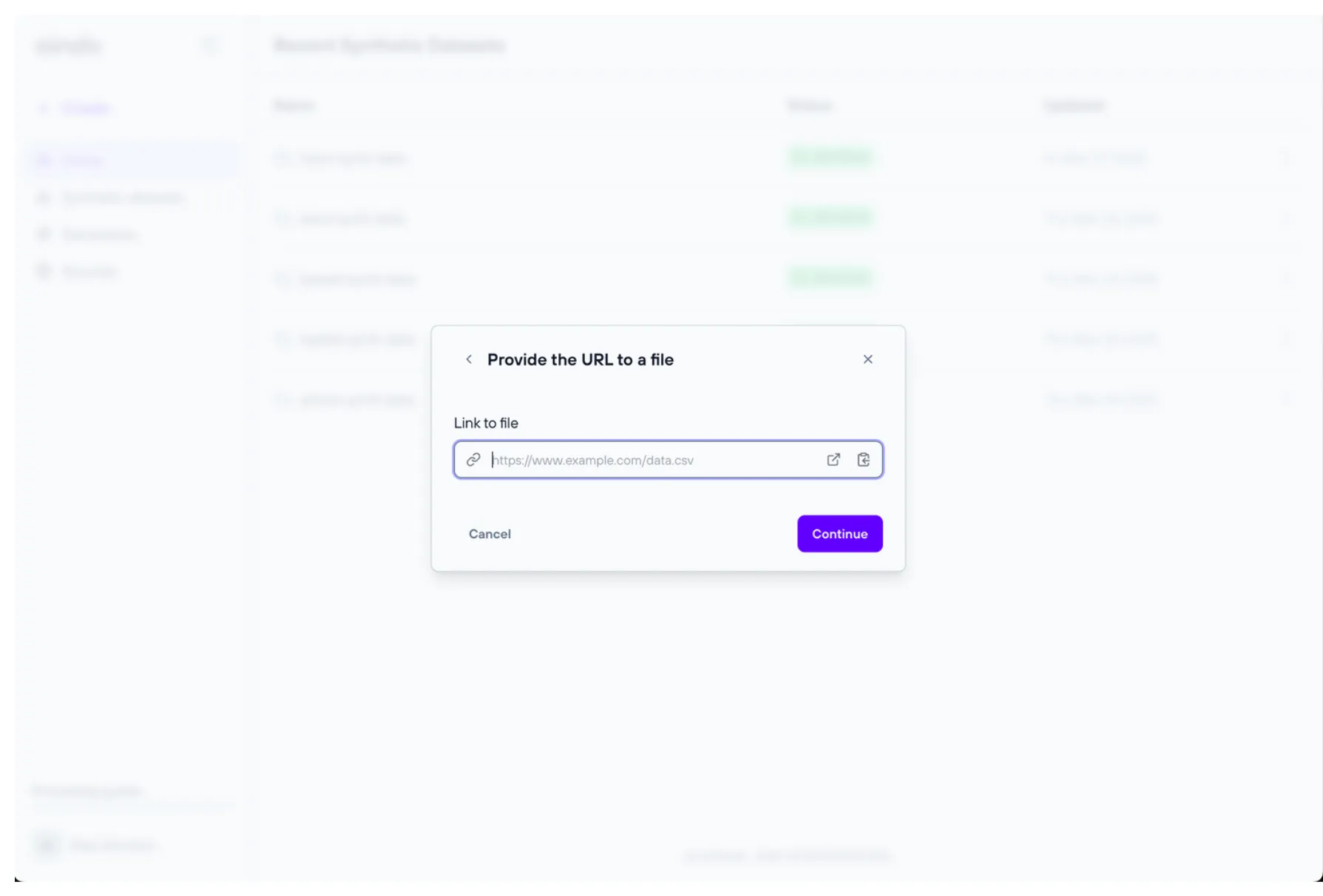
URL source
Data can also be imported through URLs, provided the landing webpage contains a table. To import a table directly from a webpage, click on “Provide the URL to a file” button. The following window will appear. Enter the URL in the text field and click on “Continue”.
Configuration steps
The source configurator allows you to review and modify some properties of the imported data.
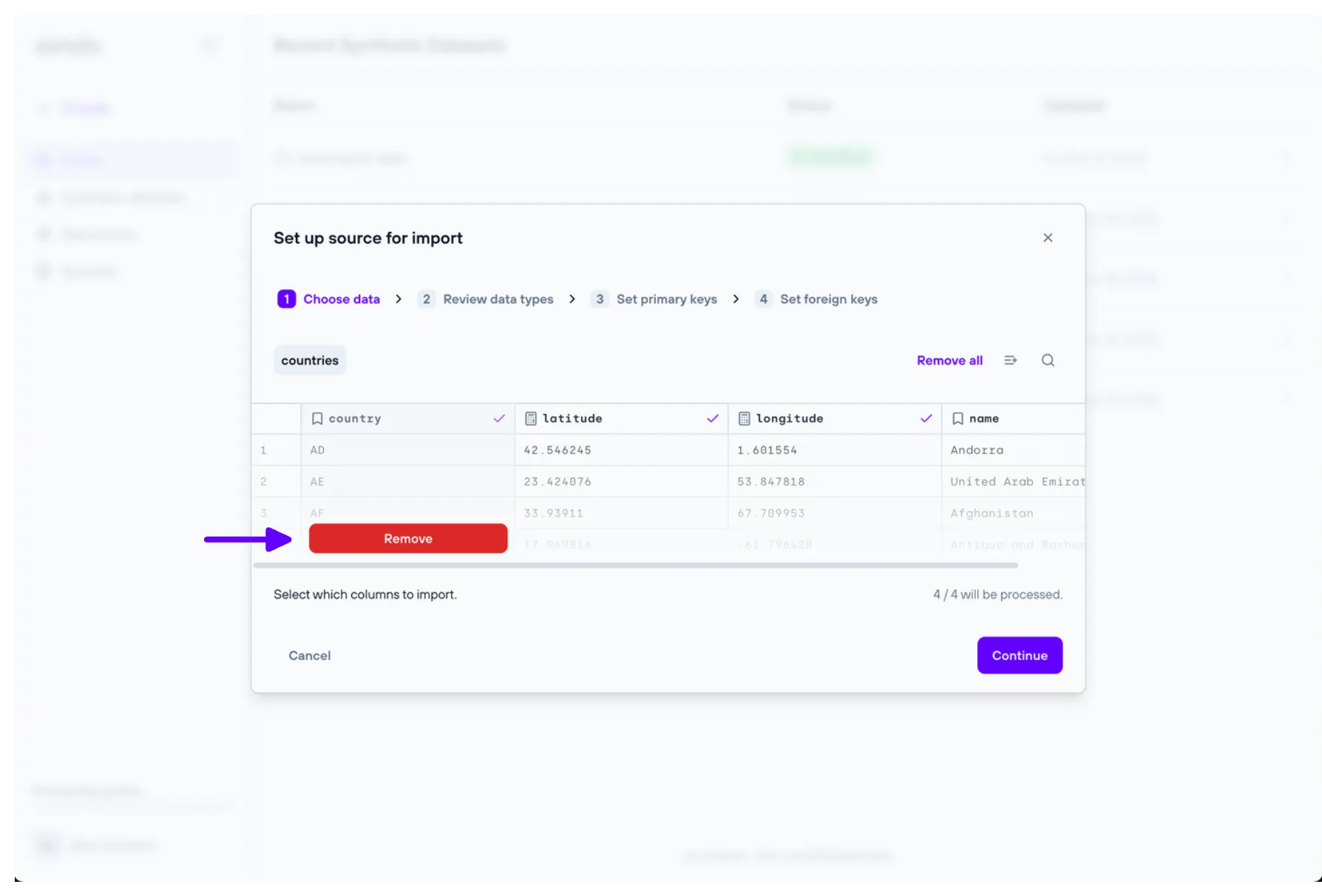
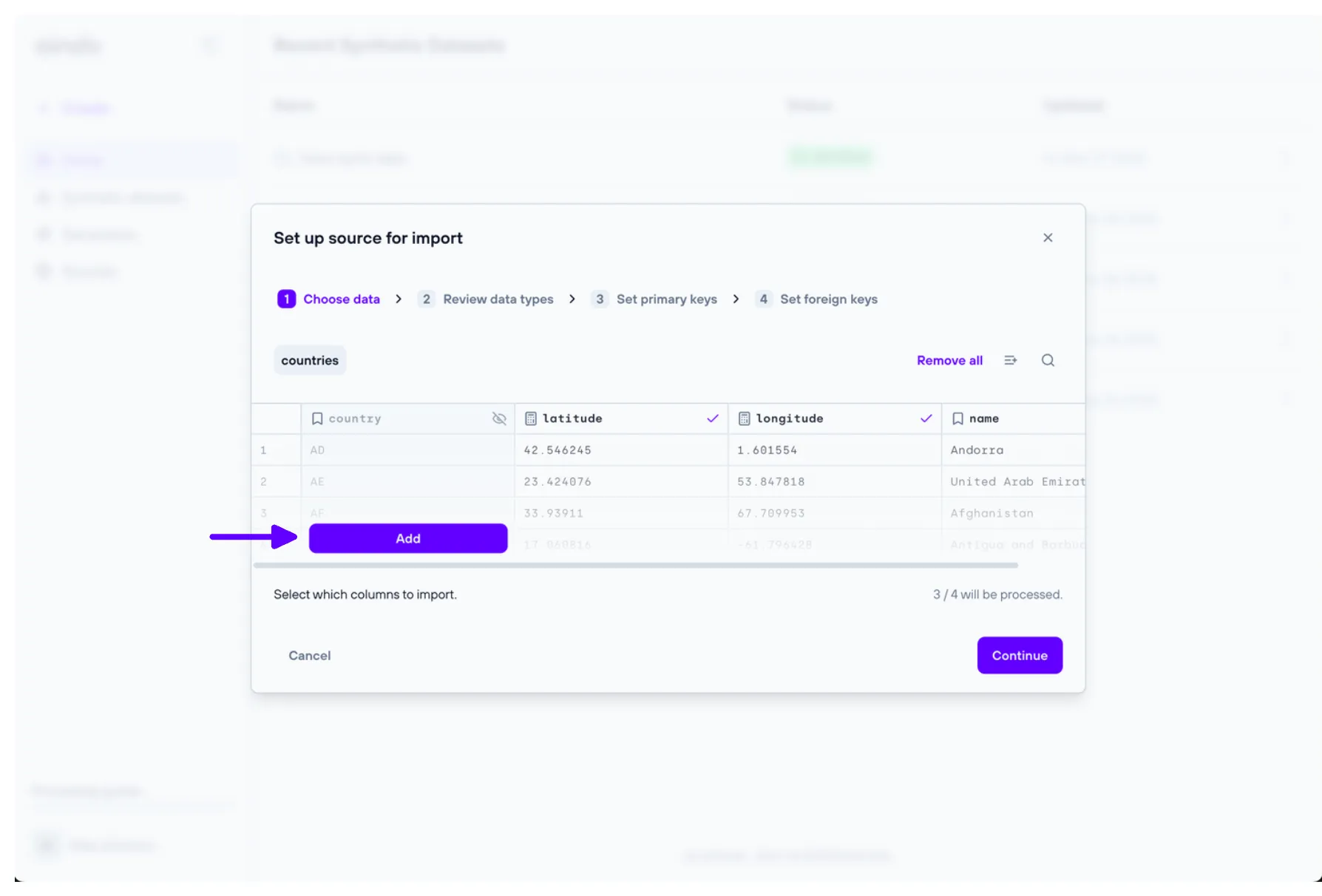
1. Choose data
The ‘Choose data’ step allows the user to include or exclude tables and/or columns from the data previously uploaded.
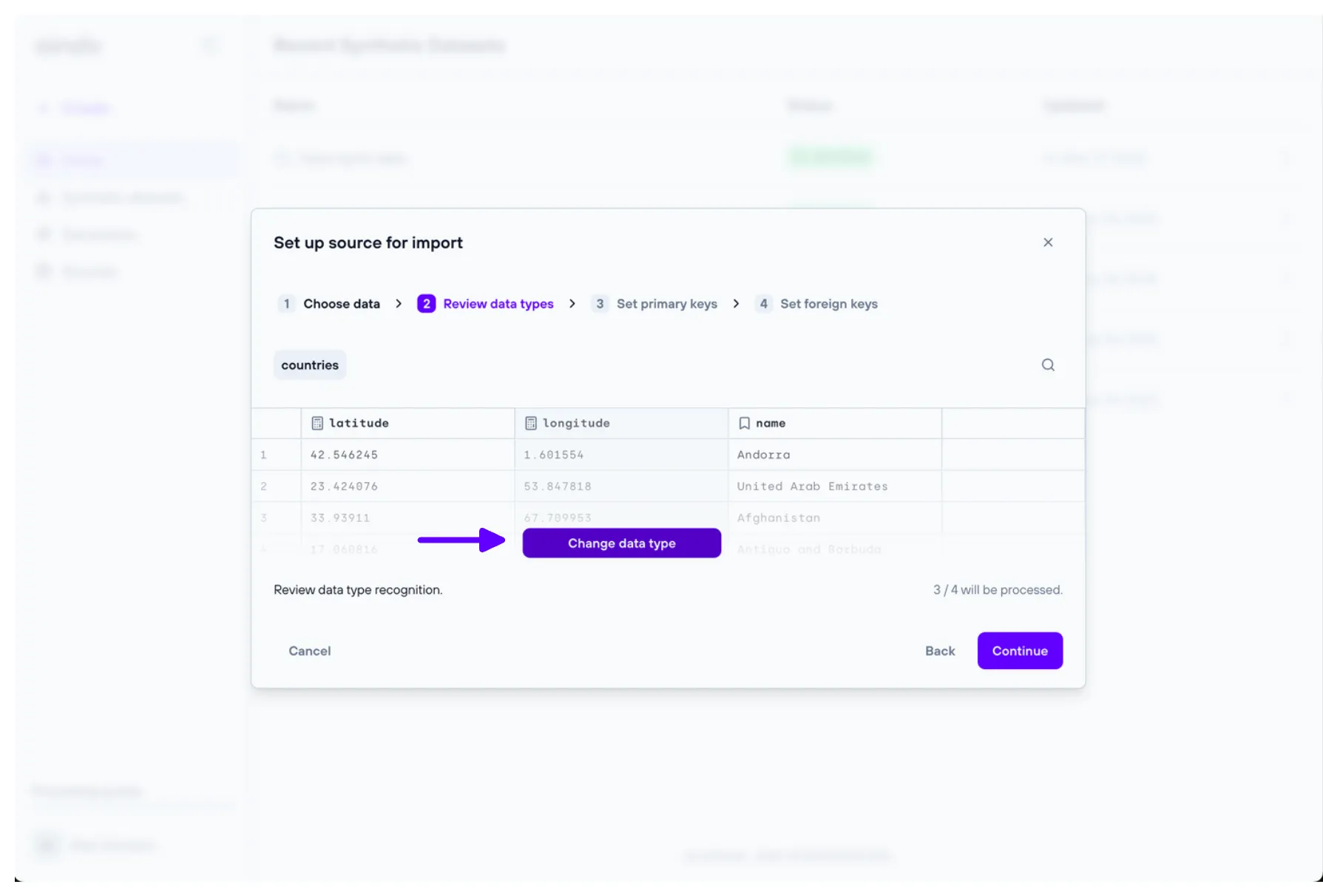
2. Review data types
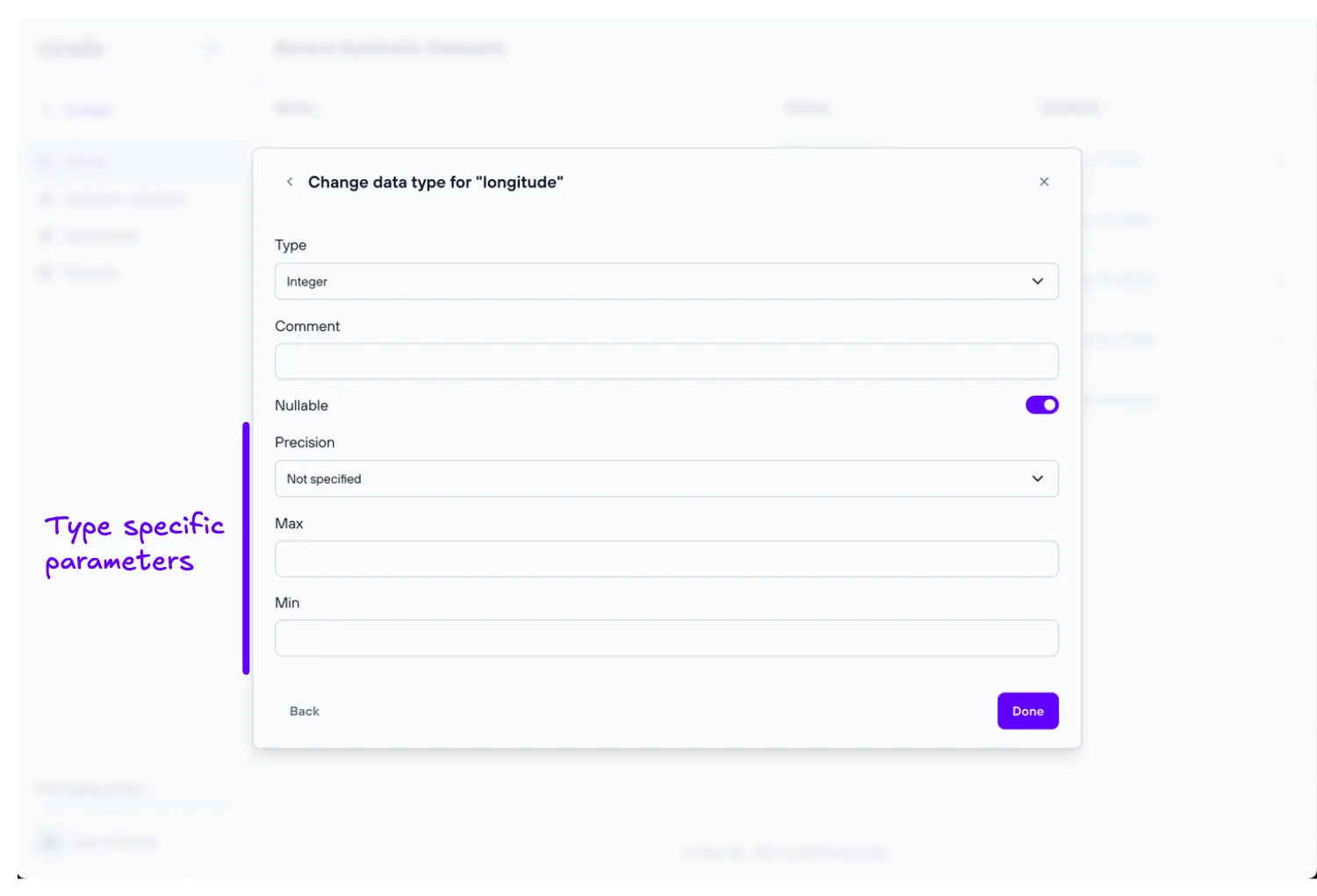
The ‘Review data types’ step allows the user to change the type of a column, choosing from the ones reviewed in the Supported data types section.
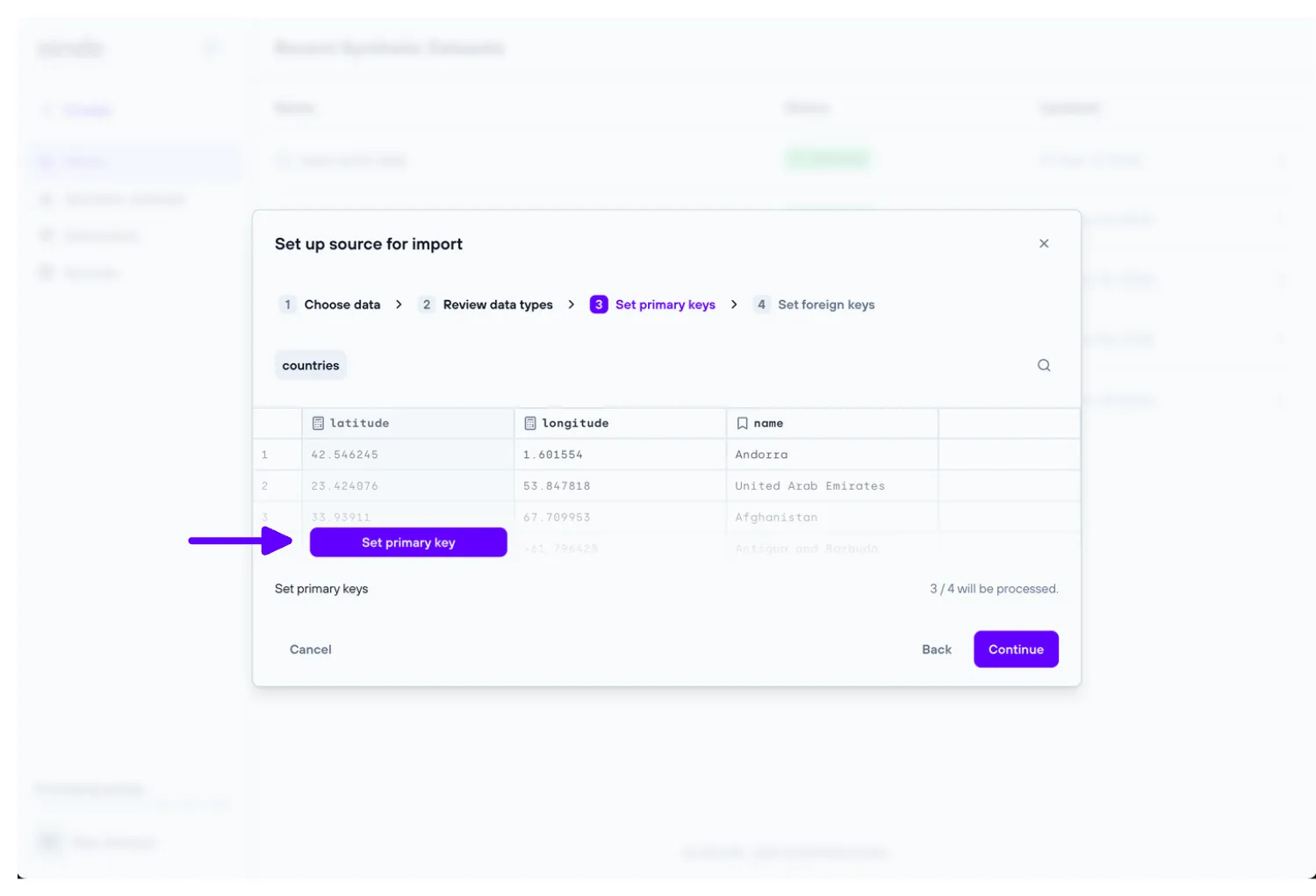
3. Set primary keys
The ‘Set primary keys’ step allows the user to set and unset primary keys for every table of the data previously uploaded.
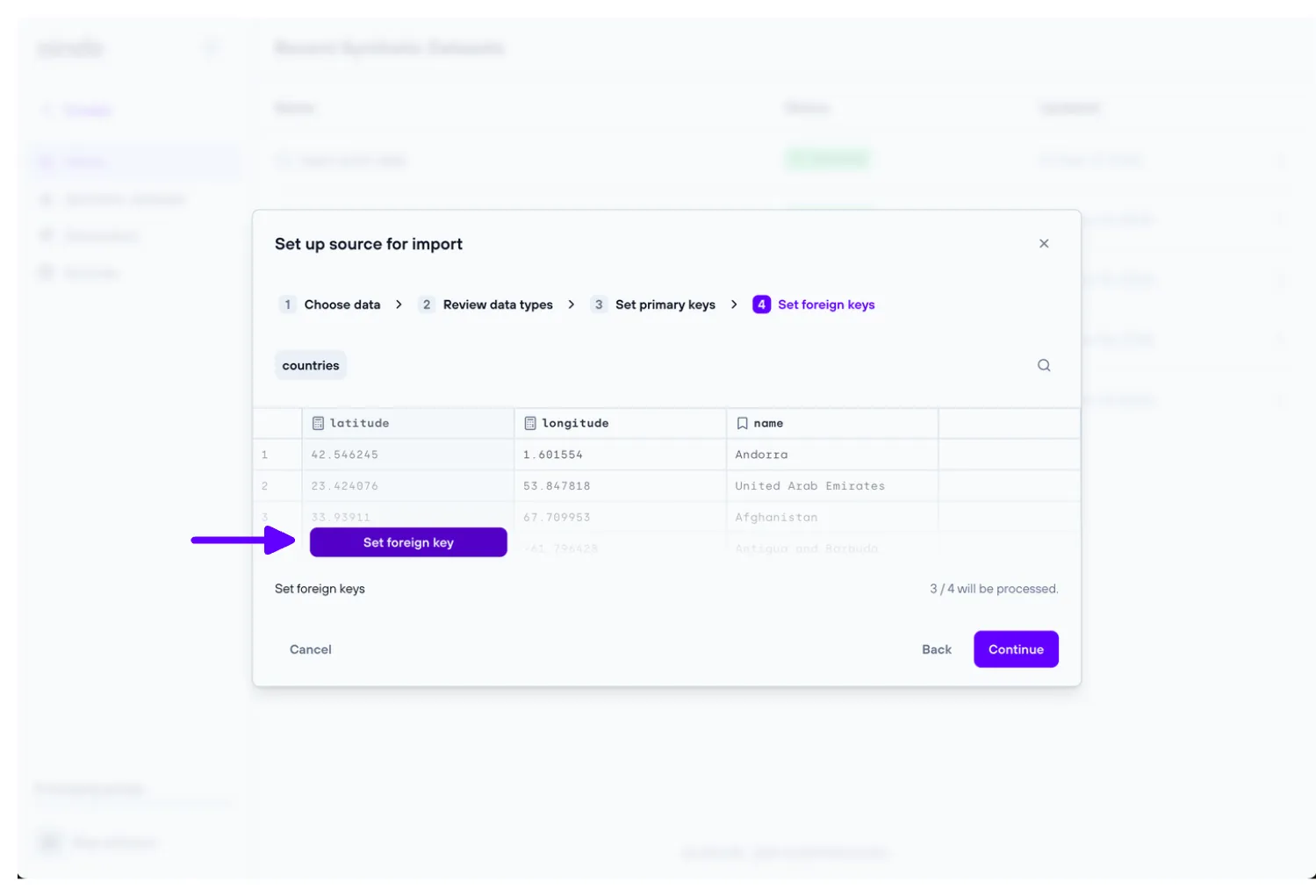
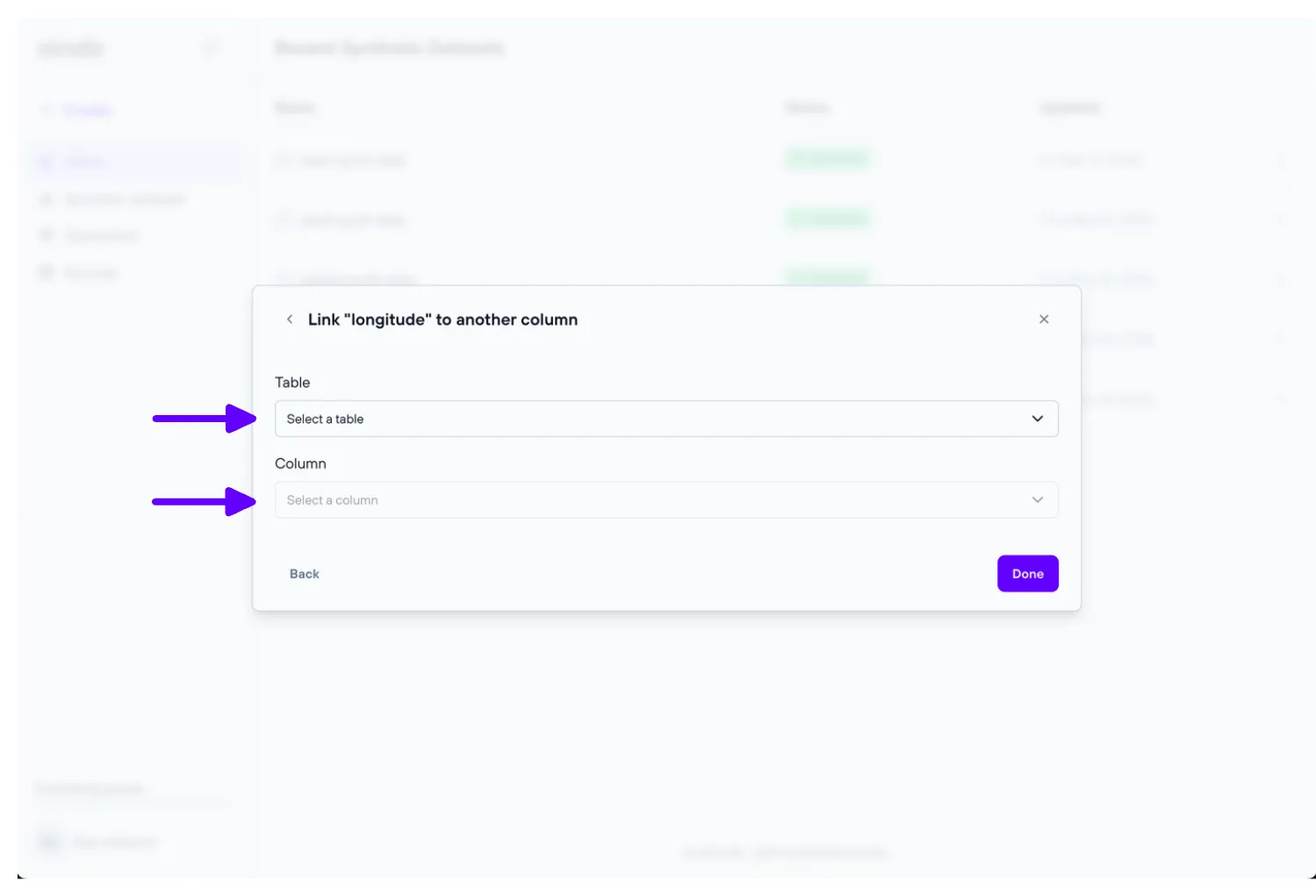
4. Set foreign keys
The ‘Set foreign keys’ step allows the user to set and unset foreign keys for every table of the data previously uploaded.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter any issues, here are some common problems and their solutions:
- File rejection: Ensure your file complies with the format requirements.
- incorrect Column Types: Use the ‘Review data types’ step to correct any misidentified column type.
- Missing Data: Check that all rows have the same number of columns.
FAQ
Q: What do I do if my file is larger than 100MB?
A: If you are working on an on-premise deployment, contact Aindo support to help you increase the size limit. If you are working on a cloud deployment, consider migrating the data to a supported database.
Q: Can I upload a file with no headers?
A: Yes you can, but the first row will be inferred as the header row.
Q: Can I use a database as source without ‘read’ permissions?
A: No, ‘read’ permissions are required so that Aindo can access the data for synthesis.